Fix clippy::bool_assert_comparison and clippy::needless_borrow, which were temporally added at crrev.com/c/3267912. Most changes are trivial. `test_should_reconnect` in vhost_user/mod.rs was deleted because the test doesn't make much sense as a unit test, because it just copies and pastes the logic of `Error::should_reconnect()`. BUG=b:205511695, b:204720423 TEST=./tools/clippy TEST=cargo test --all-features in third_party/vmm_vhost Change-Id: I664b3aa7df054871d7e127b6dffd0315f9d4c48c Reviewed-on: https://chromium-review.googlesource.com/c/chromiumos/platform/crosvm/+/3267918 Tested-by: kokoro <noreply+kokoro@google.com> Commit-Queue: Keiichi Watanabe <keiichiw@chromium.org> Reviewed-by: Chirantan Ekbote <chirantan@chromium.org> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| .buildkite | ||
| .cargo | ||
| .github | ||
| docs | ||
| src | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| Cargo.toml | ||
| CODEOWNERS | ||
| coverage_config_aarch64.json | ||
| coverage_config_x86_64.json | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| LICENSE-BSD-3-Clause | ||
| LICENSE-BSD-Chromium | ||
| PRESUBMIT.cfg | ||
| README.md | ||
vHost
A pure rust library for vDPA, vhost and vhost-user.
The vhost crate aims to help implementing dataplane for virtio backend drivers. It supports three different types of dataplane drivers:
- vhost: the dataplane is implemented by linux kernel
- vhost-user: the dataplane is implemented by dedicated vhost-user servers
- vDPA(vhost DataPath Accelerator): the dataplane is implemented by hardwares
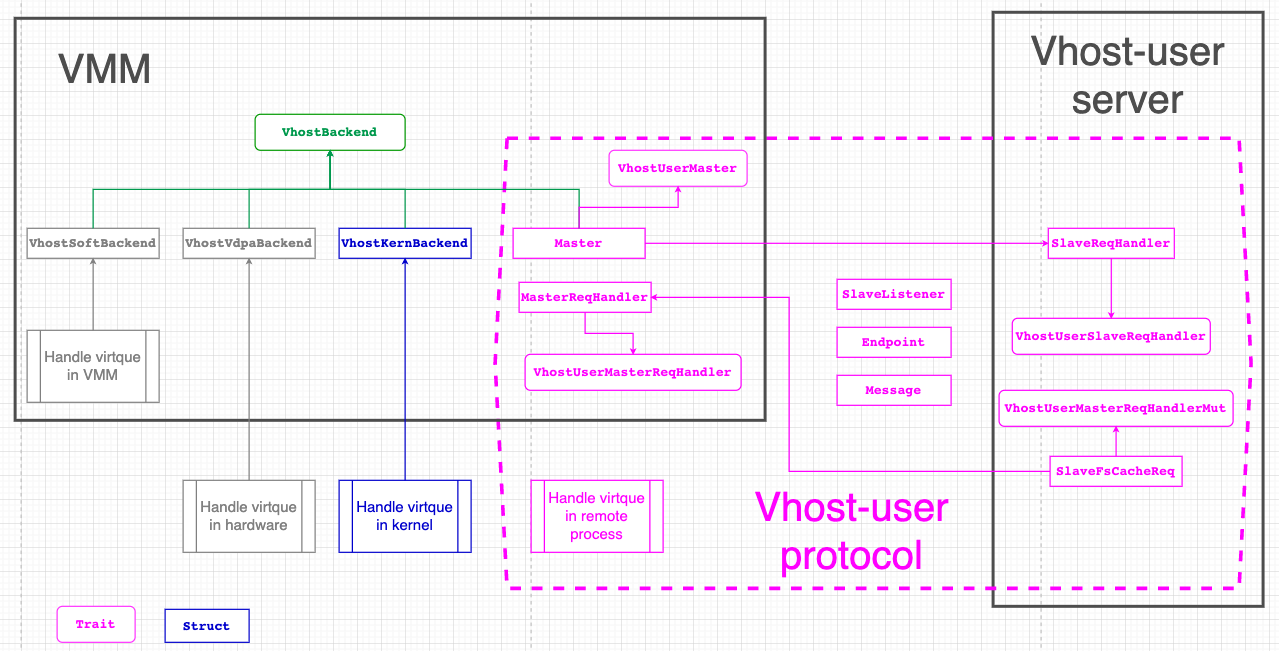
The main relationship among Traits and Structs exported by the vhost crate is as below:
Kernel-based vHost Backend Drivers
The vhost drivers in Linux provide in-kernel virtio device emulation. Normally the hypervisor userspace process emulates I/O accesses from the guest. Vhost puts virtio emulation code into the kernel, taking hypervisor userspace out of the picture. This allows device emulation code to directly call into kernel subsystems instead of performing system calls from userspace. The hypervisor relies on ioctl based interfaces to control those in-kernel vhost drivers, such as vhost-net, vhost-scsi and vhost-vsock etc.
vHost-user Backend Drivers
The vhost-user protocol aims to implement vhost backend drivers in userspace, which complements the ioctl interface used to control the vhost implementation in the Linux kernel. It implements the control plane needed to establish virtqueue sharing with a user space process on the same host. It uses communication over a Unix domain socket to share file descriptors in the ancillary data of the message.
The protocol defines two sides of the communication, master and slave. Master is the application that shares its virtqueues, slave is the consumer of the virtqueues. Master and slave can be either a client (i.e. connecting) or server (listening) in the socket communication.